Page 36 - THE ROMANIAN HEALTH CARE
P. 36
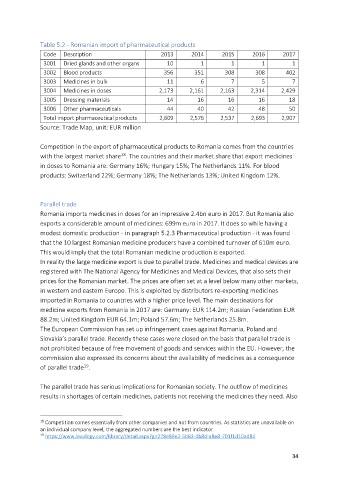
Table 5.2 - Romanian import of pharmaceutical products
Code Description 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
3001 Dried glands and other organs 10 1 1 1 1
3002 Blood products 356 351 308 308 402
3003 Medicines in bulk 11 6 7 5 7
3004 Medicines in doses 2,173 2,161 2,163 2,314 2,429
3005 Dressing materials 14 16 16 16 18
3006 Other pharmaceuticals 44 40 42 48 50
Total import pharmaceutical products 2,609 2,576 2,537 2,693 2,907
Source: Trade Map, unit: EUR million
Competition in the export of pharmaceutical products to Romania comes from the countries
18
with the largest market share . The countries and their market share that export medicines
in doses to Romania are: Germany 16%; Hungary 15%; The Netherlands 11%. For blood
products: Switzerland 22%; Germany 18%; The Netherlands 13%; United Kingdom 12%.
Parallel trade
Romania imports medicines in doses for an impressive 2.4bn euro in 2017. But Romania also
considerable amount of medicines: 699m euro in 2017. It does so while having a
exports a
modest domestic production - in paragraph 5.2.3 Pharmaceutical production - it was found
that the 10 largest Romanian medicine producers have a combined turnover of 610m euro.
This would imply that the total Romanian medicine production is exported.
In reality the large medicine export is due to parallel trade. Medicines and medical devices are
registered with The National Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices, that also sets their
prices for the Romanian market. The prices are often set at a level below many other markets,
in western and eastern Europe. This is exploited by distributors re-exporting medicines
imported in
Romania to countries with a higher price level. The main destinations for
medicine exports from Romania in 2017 are: Germany: EUR 114.2m; Russian Federation EUR
88.2m; United Kingdom EUR 64.1m; Poland 57.6m; The Netherlands 25.8m.
The European Commission has set up infringement cases against Romania, Poland and
Slovakia’s parallel trade. Recently these cases were closed on the basis that parallel trade is
not prohibited because of free movement of goods and services within the EU. However, the
commission also expressed its concerns about the availability of medicines as a consequence
19
of parallel trade .
The parallel trade has serious implications for Romanian society. The outflow of medicines
results in shortages of certain medicines, patients not receiving the medicines they need. Also
18 Competition comes essentially from other companies and not from countries. As statistics are unavailable on
an individual company level, the aggregated numbers are the best indicator.
19 https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=278e89e2-5b83-4b8d-a8e8-701f1d10ad84
34